C-reactive protein (CRP)
| About This Test |
|
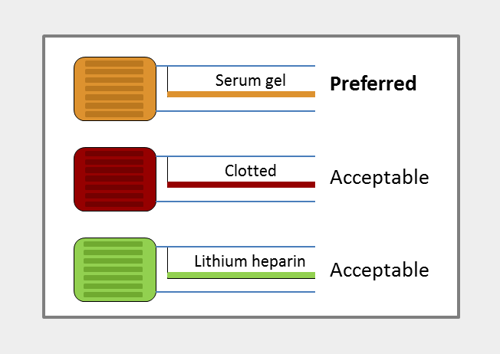
Department: Biochemistry Requirement:
Add-on requests are accepted
Turnaround Time: Within 24 hours |
Background:
Identification of inflammation and infection
CRP is a sensitive marker of the acute phase response, increasing following myocardial infarction, stress, trauma, bacterial infection, inflammation, surgery or neoplastic proliferation.
CRP concentration begins to increase 6 – 12 hours after initiation of an acute phase response, reaching a peak at around 48 hours.
CRP may also be used as a marker in monitoring patients with inflammatory conditions, such as Crohn’s disease or rheumatoid arthritis. Viral infections usually do not cause a significant increase in CRP, nor do immune diseases such as SLE and scleroderma, anaemia, polycythemia, ulcerative colitis or pregnancy.
Reference ranges:
| Age range | Reference range (mg/L) |
|---|---|
| All ages/sexes | 0 - 5 |
Derived from Tietz Fundamentals of Clinical Chemistry 5th Ed. 2001
Results outside the reference range do not necessarily indicate disease. Similarly, results within the reference range do not preclude abnormality. Please contact the Duty Biochemist for discussion of individual patient results.
Other Comments:
For more information, please see the following: CRP - Lab Tests Online
Content approved in Clinical Biochemists meeting 05.09.18